At the core of the Readiness Assurance Process (RAP) in Team-based Learning (TBL) lies the essential skill of crafting single best answer Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs). Effective MCQs hold the power to shape the entire learning experience. The days of regurgitating trivial or isolated facts are long gone, as educators now strive to develop thought-provoking questions that not only challenge learners’ understanding but also foster collaboration among them. In this blog post, we will delve into strategies to write effective MCQs for the RAP in TBL.
Why are Multiple-Choice Questions important?
Before we cover the strategies, let’s understand more about why MCQs play a crucial role in TBL. Firstly, MCQs help learners' reflect on their understanding of the key concepts and important information from the pre-work material, ensuring they focus on the essential content that prepares them for the Application phase. Additionally, during the Team Readiness Assurance Tests (TRAT), learners gain immediate feedback, allowing them to quickly gauge their understanding of the content and identify areas that may require further clarification, either from teammates or faculty. Further, the individual and team performance offer instructors an efficient means to evaluate a wide range of individual and class learners’ understanding within a short span of time. It also helps faculty to recognize gaps in knowledge that might need to be clarified in the pre-work and debrief in the session.
Components of a Multiple-Choice Question

A Multiple-Choice item consists of a question stem and a list of answer choices, collectively known as a Multiple-Choice Question. The choices within the question include multiple distractors, which are incorrect choices, and one single correct answer (Williams, 2022).
Basic Rules for Constructing Effective Multiple-Choice Items
Now let’s explore some basic rules that can elevate the quality and impact of your questions:
-
Focus each item on an important concept, principle, or complex idea, and use real-world examples. Avoid trivial facts.
-
Pose clear questions in the stem that can be answered without seeing the answer choices, avoiding irrelevant material.
-
Avoid negatively stated stems unless necessary for specific learning outcomes, such as identifying dangerous practices.
-
Ensure all alternatives are plausible, mutually exclusive, and of the same category.
-
Avoid overlap in content, present alternatives in a logical order, and maintain consistent length and clarity.
-
Exclude options like 'all of the above' or 'none of the above’, as they may allow students to guess correctly based on partial knowledge.
Using Bloom's Taxonomy to Write the Question Stem
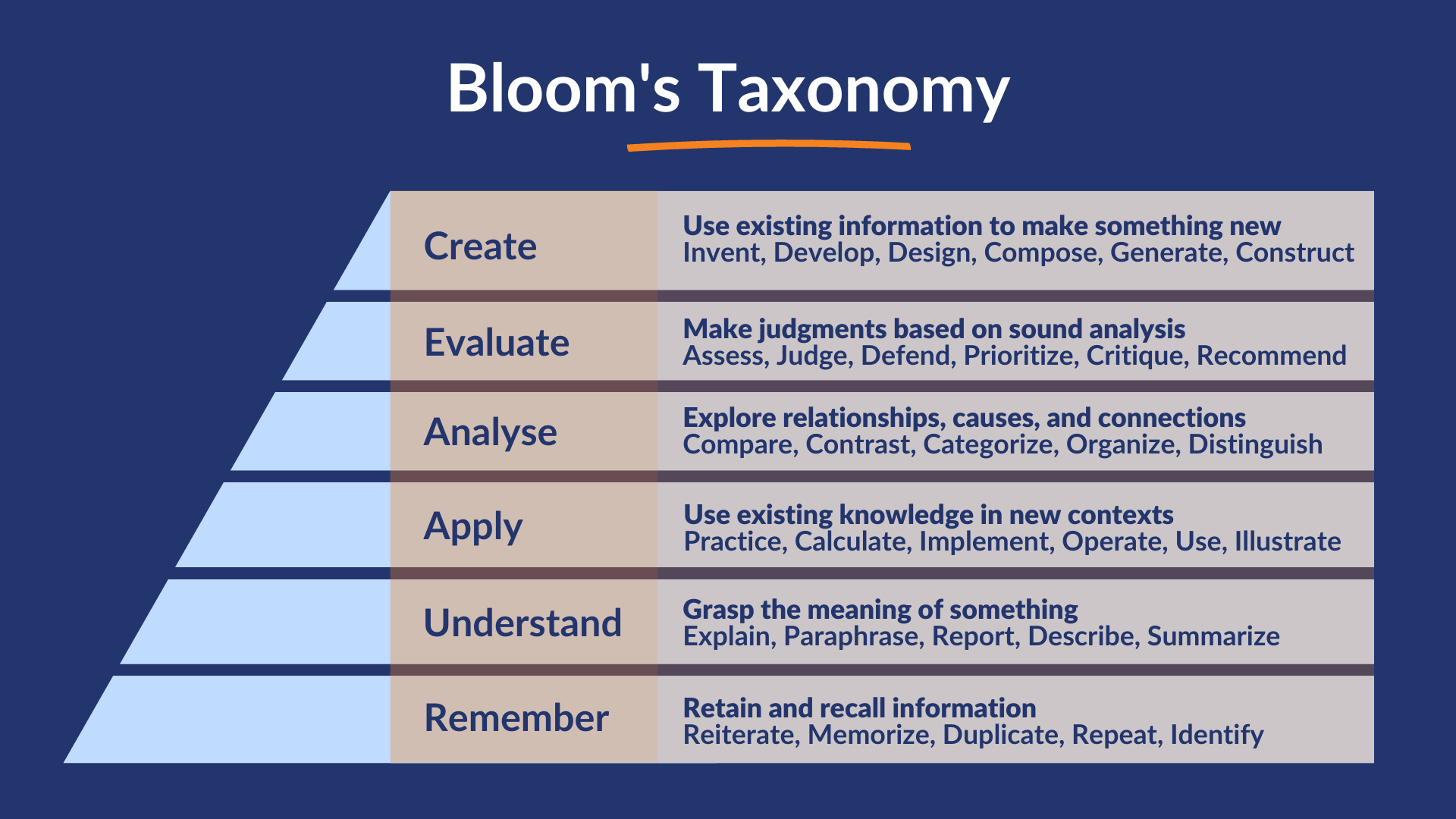
The use of verbs associated with each level of Bloom’s Taxonomy can help in constructing question stems that guide learners towards desired cognitive abilities. The most common verbs faculty use in questions stems, at the lower levels of Bloom's Taxonomy (such as Remember and Understand), are verbs like "define," "identify," "describe," or "summarize". These verbs prompt learners to recall information, understand concepts, or explain ideas, encouraging them to engage in foundational thinking.
However, higher levels of Bloom's Taxonomy (such as Apply, Analyse, Evaluate and Create), can also be used. Verbs associated with these levels become more complex and demanding. Verbs like "distinguish," "compare," "synthesize," or "analyze" prompt learners to demonstrate more advanced cognitive abilities, such as applying knowledge to real-world situations, breaking down complex problems, integrating information to create new insights, or making judgments based on criteria. The higher level is more likely to be used in crafting the Application questions, which you can learn more about here.
All in all, creating effective MCQs is an essential skill for educators implementing the RAP in Team-based Learning. MCQs have the potential to serve as strong motivators, inspiring students to actively engage in comprehensive study and preparation for TBL classes. As educators, it is crucial to take charge of this process, ensuring that the MCQs can effectively drive student participation and enhance the learning experience.